Organizations of every size are in the initial phases of modernizing their IT infrastructure to transform themselves into digital businesses. One of the key themes for that modernization is the utilization of Flash-base storage technologies in the data center to achieve such benefits as peak performance, consistent operations levels, and higher throughput rates.
However, just because you have Flash storage doesn’t mean your IT application is going to perform miraculously. Getting the most out of your Flash environment takes understanding your application requirements, operating characteristics, SLAs and your entire application ecosystem. It takes careful analysis of your use case, workload patterns, data services, capacity needs, and operational skills to determine which Flash platform will provide the desired results. The goal of this blog is to provide a set of guidelines from which organizations can make informed decisions.
Fortunately, we at Dell IT have a rich Flash storage portfolio and, working with our engineering teams, we have put together the Top 10 Tips and Tricks on how you can optimize your Flash environment in today’s cloud-enabled, Big Data focused, IT world. These platforms, products, tools and best practices will help you make the most of your Flash investments irrespective of the modernization stage you are at.
After all, today’s modern data center demands the speed and agility of Flash more and more. And there is an extensive array of products—such as DellEMC’s end-to-end Flash portfolio—that address this growing need.
When Flash technology was first developed more than a decade ago, it was considered premium storage reserved for only the most critical high-performance computing and database needs that warranted its expense. However, technical innovations in Flash, including the advancement of NAND Flash— a type of compact memory device which provides high density storage— have changed that. NAND has not only led to a decrease in unit price for Flash over the years, but also now provides increased capacities and greater endurance levels which meet and exceed enterprise reliability requirements. Accompanying advances in interface speeds and protocols have made Flash, a first choice in storage for the modern data center.
These technological, financial, and operational breakthroughs paved the way for All Flash Arrays, which are built on innovative Scale-Out Architectures, coupled with intelligent software. All Flash arrays incorporate inline data reduction and instant data copy features to provide greater economics, and rich data services such as replication and encryption, sustained performance during failures, and deep integration with hypervisors such as VMware ESXi have made them a natural choice for deploying business critical to mission critical workloads.
You could say the IT shops have progressed from “Why Flash?” to “Some Flash,” to “Start with Flash.” Much like the server world transitioned from physical to virtual in 2012, 2016 is the year when transactional workloads have transitioned to Flash-based storage.
I won’t go into the details of our tips, which are spelled out in the above link. In general, they will hopefully help you with a range of practices, including provisioning Flash capacity, taking advantage of a range of workload planning tools, integrating and protecting your data, testing and analyzing solution performance, and much more.
Revving up our ERP with Flash
What I will share with you is a use case that demonstrates the potential benefits of leveraging Flash. In early 2015, EMC IT migrated a major module of its SAP ERP system from tiered Storage to all-Flash storage. The ERP system runs the company’s core systems of record.
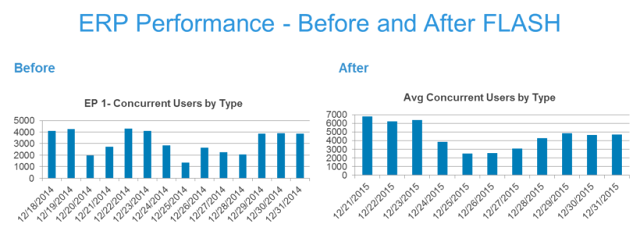
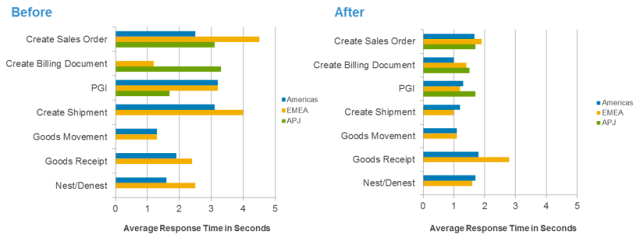
We used the best practices listed in the tips referenced above to effectively size, build and deploy Flash in our ERP environment. The benefits were substantial. Before we implemented Flash, our ERP system had approximately 4,215 peak users at the end of 2014. The time it took to execute an individual transaction was between 2-4 seconds, with an average of 3 seconds (please note that the response time was measured at the business app layer which contains the logic, not at storage subsystem). After we completed the transition to Flash in Q4 2015, the system was able to sustain approximately 7000 users and to complete an individual transaction in half the time of 1.5 seconds, even though our peak user activity increased by 66 percent.
However, just because you have Flash storage doesn’t mean your IT application is going to perform miraculously. Getting the most out of your Flash environment takes understanding your application requirements, operating characteristics, SLAs and your entire application ecosystem. It takes careful analysis of your use case, workload patterns, data services, capacity needs, and operational skills to determine which Flash platform will provide the desired results. The goal of this blog is to provide a set of guidelines from which organizations can make informed decisions.
Fortunately, we at Dell IT have a rich Flash storage portfolio and, working with our engineering teams, we have put together the Top 10 Tips and Tricks on how you can optimize your Flash environment in today’s cloud-enabled, Big Data focused, IT world. These platforms, products, tools and best practices will help you make the most of your Flash investments irrespective of the modernization stage you are at.
Flash Evolution
After all, today’s modern data center demands the speed and agility of Flash more and more. And there is an extensive array of products—such as DellEMC’s end-to-end Flash portfolio—that address this growing need.
When Flash technology was first developed more than a decade ago, it was considered premium storage reserved for only the most critical high-performance computing and database needs that warranted its expense. However, technical innovations in Flash, including the advancement of NAND Flash— a type of compact memory device which provides high density storage— have changed that. NAND has not only led to a decrease in unit price for Flash over the years, but also now provides increased capacities and greater endurance levels which meet and exceed enterprise reliability requirements. Accompanying advances in interface speeds and protocols have made Flash, a first choice in storage for the modern data center.
These technological, financial, and operational breakthroughs paved the way for All Flash Arrays, which are built on innovative Scale-Out Architectures, coupled with intelligent software. All Flash arrays incorporate inline data reduction and instant data copy features to provide greater economics, and rich data services such as replication and encryption, sustained performance during failures, and deep integration with hypervisors such as VMware ESXi have made them a natural choice for deploying business critical to mission critical workloads.
You could say the IT shops have progressed from “Why Flash?” to “Some Flash,” to “Start with Flash.” Much like the server world transitioned from physical to virtual in 2012, 2016 is the year when transactional workloads have transitioned to Flash-based storage.
I won’t go into the details of our tips, which are spelled out in the above link. In general, they will hopefully help you with a range of practices, including provisioning Flash capacity, taking advantage of a range of workload planning tools, integrating and protecting your data, testing and analyzing solution performance, and much more.
Revving up our ERP with Flash
What I will share with you is a use case that demonstrates the potential benefits of leveraging Flash. In early 2015, EMC IT migrated a major module of its SAP ERP system from tiered Storage to all-Flash storage. The ERP system runs the company’s core systems of record.
We used the best practices listed in the tips referenced above to effectively size, build and deploy Flash in our ERP environment. The benefits were substantial. Before we implemented Flash, our ERP system had approximately 4,215 peak users at the end of 2014. The time it took to execute an individual transaction was between 2-4 seconds, with an average of 3 seconds (please note that the response time was measured at the business app layer which contains the logic, not at storage subsystem). After we completed the transition to Flash in Q4 2015, the system was able to sustain approximately 7000 users and to complete an individual transaction in half the time of 1.5 seconds, even though our peak user activity increased by 66 percent.
Alternatively, when the metrics were collected from the database side, Flash provided significant reduction of response times, from 6 to 8 milliseconds to 1 to 1.5 milliseconds at peak utilization levels. Database CPU time increased from approximately 30 percent to 69 percent, which helped achieve better utilization of resources.
Going forward, we will be making investments to transition from disk-based storage to Flash, to gain long-term efficiencies in other critical business systems.
Flash is a disruptive technology and should be used to your organization’s advantage. Some of the earlier concerns of cost, capacity and wear are no longer relevant. Full benefits of virtualization and consolidation of applications cannot be achieved unless underlying storage technology meets the demanding needs of agile businesses. Combined with reduced power, cooling and operational costs of meeting SLAs, a data center with Flash-based foundation will provide long-term sustained benefits.




0 comments:
Post a Comment